Today, with increasing digitization, cyber threats are abundant, it’s crucial to prioritize risk management in cybersecurity. The outcomes of a cyber attack can be severe, including financial losses, harm to reputation, data breaches, and disrupted business operations. Moreover, with more reliance on information systems as part of digital transformation, it’s essential to have reliable Cybersecurity solution providers for robust risk management practices.
The statistics speak for themselves, highlighting the urgency and significance of prioritizing risk management in cybersecurity:
- According to Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are predicted to increase by 15% each year for the next five years. This means that by 2025, the yearly cost is estimated to be USD 10.5 trillion, a significant increase from the USD 3 trillion cost in 2015.
- According to IBM reaching an all-time high, the cost of a data breach averaged USD 4.35 million in 2022.
- A survey by IBM Security and the Ponemon Institute found that the global average data breach cost was $4.24 million in 2021, with an average of 3.5 million records exposed.
The numbers are concerning and show how much danger organizations are exposed to in the digital world. Therefore, organizations must implement robust risk management practices to protect their essential information, comply with regulations, and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
In the article, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts of risk management in cybersecurity, and its key components, highlight best practices and discuss the benefits organizations can reap by embracing this critical discipline.
The Fundamentals of Risk Management in Cybersecurity
To comprehend risk management in cybersecurity, we must first understand its fundamental concepts and terminology. So let’s explore some essential terms:
1.1 Threats: These are potential dangers that can exploit vulnerabilities in information systems. Cybersecurity Threats can manifest in various forms, such as malware, phishing attacks, data breaches, or even insider threats.
1.2 Vulnerabilities: These refer to weaknesses or flaws in information systems that threats can exploit. Vulnerabilities can arise due to misconfigurations, software bugs, or inadequate security measures.
1.3 Risk: In cybersecurity, risk refers to the probability and consequences of a threat taking advantage of a weakness. It quantifies the possible adverse effects or destruction to a company’s data and resources.
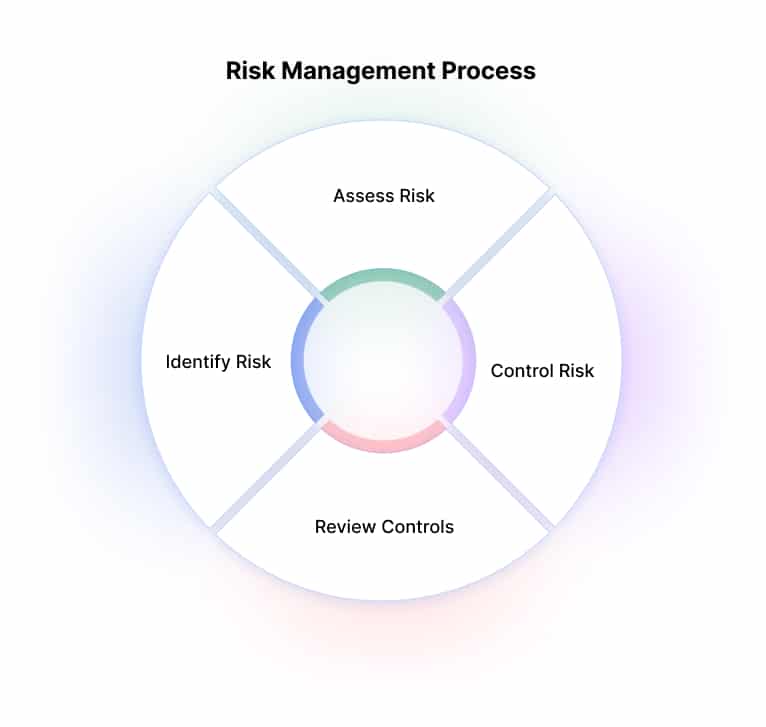
The Components of Risk Management in Cybersecurity
Effective risk management in cybersecurity involves a systematic process comprising several key components.
- Risk Assessment: To effectively manage risk, it is crucial to conduct thorough risk assessments. This involves recognizing and estimating potential risks to the organization’s information assets and assessing the likelihood and impact of threats exploiting vulnerabilities. Techniques like vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and threat modeling are used to understand the risk landscape comprehensively.
During a risk assessment, organizations identify their critical assets, assess their vulnerabilities, and evaluate potential threats that may exploit those vulnerabilities. Organizations can prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources effectively by conducting meticulous analysis.
Example: To prevent a potential data breach, a financial institution can update its outdated software, enhance its database security measures, and follow secure coding practices after identifying vulnerability to SQL injection attacks.
2. Risk Mitigation: Once risks are identified through the assessment phase, the next crucial step is to implement controls and safeguards to reduce the likelihood or impact of the identified risks. Risk mitigation involves a range of technical and non-technical measures aimed at minimizing vulnerabilities and strengthening the overall security posture.
To reduce risks, use firewalls, encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection. In addition, educate employees on security best practices and establish clear policies and procedures. This helps prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and other security breaches.
Example: An e-commerce company may implement two-factor authentication (2FA) for customer accounts to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and prevent account takeovers. By requiring an additional verification step, such as a unique code sent to the user’s mobile device, the company adds an extra layer of protection against compromised passwords or stolen credentials.
3. Risk Monitoring: Managing risk is a continuous process that requires constant monitoring of control effectiveness and emerging threats. Regular security assessments, vulnerability scanning, log analysis, and incident response planning are necessary to ensure this.
Example: A healthcare provider continuously monitors their network traffic and detects an unusual spike in outbound data transfers. Prompt investigation reveals a compromised workstation attempting to exfiltrate patient data, enabling them to take immediate action to contain the incident.
4. Risk Communication: Clear and effective communication is vital for successful risk management in cybersecurity. Stakeholders, including senior management, IT teams, and end-users, must be kept informed about potential risks, mitigation strategies, and the importance of adhering to security policies and procedures.
Example: An organization conducts regular security awareness training sessions to educate employees about phishing attacks, the risks associated with clicking on suspicious links, and the importance of reporting suspicious emails to the IT department.
The Importance of Risk Management in Cybersecurity
Protection of Valuable Assets
Businesses possess significant assets, such as customer data, intellectual property, trade secrets, and financial information. However, these assets are often targeted by cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or malicious purposes. To prevent this, businesses can implement risk management practices to identify and assess potential threats and weaknesses in their systems.
With appropriate safeguards, such as firewalls, encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, businesses can protect their valuable assets from unauthorized access, theft, or compromise.
Mitigation of Financial Losses
Cybersecurity attacks such as data breaches or ransomware attacks can cause businesses to experience substantial financial losses. Investigating the incident, implementing remediation measures, legal fees, regulatory penalties, potential lawsuits, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust can all contribute to these losses.
However, by proactively managing risks and implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of such incidents, thereby minimizing potential financial losses.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
In cybersecurity, managing risks involves complying with industry regulations and data protection standards. There are different regulatory frameworks, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), or industry-specific standards, like Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), that require businesses to protect personal and sensitive data. Non-compliance with these regulations carries severe legal and financial consequences.
Preservation of Business Continuity
Cybersecurity incidents can disrupt critical business operations and lead to costly downtime. A successful attack or system compromise can render systems inaccessible, disrupt supply chains, interrupt customer services, and result in financial losses.
Risk management in cybersecurity involves identifying potential threats, vulnerabilities, and weaknesses in the organization’s infrastructure and implementing appropriate safeguards to ensure business continuity. This may include implementing backup and recovery mechanisms, disaster recovery plans, and incident response protocols.
Preservation of Customer Trust and Reputation
A single data breach or security incident can significantly erode customer trust and damage an organization’s reputation. Implementing effective risk management practices demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer data and instills stakeholder confidence.
Best Practices for Risk Management in Cybersecurity
Managing cyber risks proactively can help organizations minimize security incidents, assure customers of data confidentiality and integrity, and maintain a positive reputation in the marketplace. Such measures foster customer loyalty and attract new customers who prioritize security in their business relationships.
By following best practices, organizations can proactively identify and address cyber risks, implement appropriate controls, and enhance their security posture. Let’s explore the best cybersecurity risk management practices that can help businesses strengthen their defenses and safeguard against cyber threats.
Conduct Comprehensive Risk Assessments
A thorough risk assessment forms the foundation of effective risk management in cybersecurity. It involves identifying and evaluating potential risks, vulnerabilities, and impacts on the organization’s information assets.
Businesses can enhance their security by conducting thorough risk assessments. Organizations can prioritize mitigation efforts by recognizing potential threats, evaluating their likelihood and potential impact, and determining vulnerabilities. This understanding allows for targeted strategies and effective allocation of resources to mitigate risks.
Implement a Risk-Based Approach
A risk-based approach involves prioritizing and allocating resources based on the risk status associated with typical assets or processes. But, of course, not all chances are equal, and organizations must focus on addressing the most critical risks first. This approach ensures that limited resources are utilized efficiently and that the most significant risks are handled promptly, reducing the overall exposure to cyber threats.
Establish Robust Security Controls
To keep cyber threats at bay and minimize risks, it is crucial to have strong security measures in place. These measures may include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, secure authentication mechanisms, access controls, and encryption. It is crucial to ensure that these security controls align with the identified risks and the organization’s level of risk tolerance.
Additionally, they should follow industry best practices and meet regulatory requirements. Finally, monitoring and updating these controls is essential to ensure their effectiveness and adapt to new threats.
Develop an Incident Response Plan
Even with proactive risk management measures, organizations may still face security incidents. Having a clear incident response plan is crucial for reducing the impact of an incident and ensuring a quick response. The plan should outline the steps to be taken during and after an incident, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery. Routine testing and updating of the happening response plan are essential to ensure its effectiveness and address any changes in the threat landscape.
Provide Ongoing Employee Training and Awareness
Employees play a crucial role in cybersecurity risk management. They are usually the first line of defense against cyber threats and can inadvertently become targets or vectors for attacks. Regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs equip employees with the ability and skills to identify and respond to potential risks. This includes educating them on phishing attacks, password security, social engineering, and safe internet practices. Ongoing training ensures that employees remain vigilant and aware of the evolving threat landscape.
Regularly Monitor and Assess Security Controls
Regular monitoring and assessment of security controls are essential to identify any weaknesses or gaps in the organization’s defenses. This can be achieved through continuous monitoring tools, penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and security audits.
Businesses can stay secure by monitoring and assessing their security controls. This helps them quickly identify and address any vulnerabilities and make necessary updates or patches.
Various Cyber Risk Management Frameworks
Some of the most commonly used cyber risk management frameworks include:
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework: NIST made a cybersecurity framework with five core functions: Identity, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. This helps organizations manage cybersecurity risks effectively.
- ISO 27001: It is a global standard for managing information security risks. It provides a structured approach for organizations to identify, assess, and handle security threats. The standard emphasizes continual improvement through risk assessment, treatment, and monitoring.
- COSO ERM: The ERM framework by COSO helps organizations recognize and handle risks, including cyber threats. It emphasizes the need to integrate risk management into the overall plan.
- FAIR: FAIR is a reliable method for managing cybersecurity risks. It assesses and quantifies potential loss events to inform resource allocation for risk mitigation.
- OCTAVE: OCTAVE is a framework for managing cybersecurity risks considering the operational context. It identifies critical assets, threats, and vulnerabilities to create effective risk mitigation strategies.
Also check: The Role of Blockchain In Revolutionizing Cybersecurity
Over to You!
When it comes to cybersecurity for startups, SMEs, they must have a secure environment to conduct their business without any potential online risks. To ensure uninterrupted operations, protect valuable assets, and gain customer trust, startups must prioritize risk management and implement effective cybersecurity practices. They should also regularly test and update their plan to address emerging threats.
In general, cybersecurity is a critical aspect for both startups and established businesses. By prioritizing risk management, implementing robust security measures, training employees, and staying vigilant, startups can establish a secure foundation for growth in the digital landscape. It’s also recommended to seek out a reliable cybersecurity solution company for ongoing updates and security.
Frequently Asked Questions
The cost of managing cybersecurity risk in the information age can vary significantly depending on the size of the organization, its level of risk exposure, and the specific security measures implemented. Generally, investing in cybersecurity is essential to protect sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and avoid potential financial losses from cyberattacks. Costs may include hiring cybersecurity experts, implementing robust security technologies, conducting regular audits, and providing employee training. While there is an initial investment, the potential costs of data breaches or cyber incidents far outweigh the expenses of proactive risk management.
Risk management in cybersecurity involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats and vulnerabilities to an organization’s information systems, networks, and data. It is a systematic approach that helps organizations proactively safeguard their digital assets and sensitive information from cyberattacks. By analyzing risks, implementing security measures, and monitoring for emerging threats, businesses can effectively protect themselves against cyber threats and reduce the impact of potential incidents.
The cybersecurity managing risk in the information age online short course is designed to provide participants with essential knowledge and skills to identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity risks in today’s digital landscape. Through interactive online modules, learners will understand the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices to protect sensitive information and critical assets. This course is suitable for individuals seeking to enhance their cybersecurity awareness and professionals looking to strengthen their organization’s security posture.
Risk management in cybersecurity refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats and vulnerabilities to an organization’s information systems, data, and networks. It involves a systematic approach to understanding the likelihood and potential impact of cyberattacks, as well as implementing measures to minimize or control these risks. By employing risk management strategies, businesses can safeguard their digital assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical information, reducing the chances of cybersecurity incidents and their potential consequences.
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to achieve business objectives and protect assets. It involves analyzing uncertainties and implementing strategies to minimize negative impacts while maximizing opportunities.
As an AI language model, I don’t have access to real-time data, including the specific cost of the “Harvard Cybersecurity Managing Risk in the Information Age” program. Costs for academic programs can vary and are subject to change over time. For accurate and up-to-date information regarding the program’s cost, it is recommended to visit Harvard University’s official website or contact their admissions or cybersecurity department directly.