The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and with the rise of technology, there’s a new player in the field: the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT in healthcare uses connected devices and sensors to collect data. It analyzes the data to enable providers to make better decisions and give better care.
IoT in healthcare has immense potential to improve patient care, reduce costs, and create a more efficient healthcare system. But, there are challenges. These include security and privacy concerns, interoperability issues, and regulatory compliance.
Healthcare providers and policymakers must invest in IoT technology. They must also promote its adoption. This is needed to fully realize its potential. In this blog, we’ll dive deeper into the world of IoT in healthcare and explore how it’s already transforming the industry for the better.

How is IoT used in healthcare?
Imagine you’re driving a car on a long journey. You’re cruising along, but suddenly you notice the fuel gauge dropping rapidly. Without any additional information, you’re left with the uncertainty of when and where you’ll be able to refuel.
Now, imagine if your car was equipped with an IoT system that tracked your fuel levels, your location, and the nearest gas stations. The system could even alert you when you’re running low on fuel and guide you to the nearest station. This is similar to how IoT in healthcare works.
IoT in healthcare involves the use of connected devices and sensors that gather data from patients in real time. This data can include vital signs, medication adherence, and other health-related information.
The IoT device monitoring system then analyzes this data and provides healthcare providers with insights that help them make informed decisions about patient care. This lets providers monitor patients from afar. They can track their progress and predict possible health issues.
The car’s IoT system tracks fuel and location. IoT in Healthcare tracks patient health. It gives valuable insights to providers. Thus, IoT helps in patient care. It lets healthcare providers give more personalized and efficient care.
Importance of IoT in healthcare
The use of IoT in healthcare is becoming increasingly important, and the statistics reflect this trend:
- The IoT remote monitoring market is on the rise. In 2020, the global remote patient monitoring market was valued at $31.8 billion, and it is projected to reach $117.1 billion by 2027.
- The use of IoT in healthcare can lead to significant cost savings. A study by Accenture estimated that IoT could save the healthcare industry $300 billion per year. Moreover, It would do this by improving efficiency and cutting waste.
- IoT in healthcare can improve patient outcomes. The research found that remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions using IoT devices led to a 50% reduction in hospital readmissions.
- IoT-enabled medical devices are becoming increasingly prevalent. In 2020, it was estimated that there were 500 million IoT medical devices in use worldwide. This number is expected to grow to 1.87 billion by 2025.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of IoT in healthcare. A report by Frost & Sullivan says the pandemic caused a 60% rise in telehealth adoption. Telehealth relies heavily on IoT devices for remote monitoring.
These statistics demonstrate the growing importance of IoT in healthcare. IoT is set to transform the healthcare industry. Additionally, It will do this by improving patient outcomes, cutting costs, and boosting efficiency.

What are the benefits of IoT in healthcare?
The benefits of IoT in healthcare are vast and can lead to improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and increased operational efficiency. Here are some of the key benefits of IoT in healthcare:
-
Improved patient care and outcomes:
IoT in healthcare can improve patient care and outcomes by providing healthcare providers with real-time patient data. This allows for early detection of potential health issues and timely intervention, improving patient outcomes.
For example, smartwatches are wearable IoT devices. They can monitor patients’ heart rates and send alerts to healthcare providers if there are irregularities. This can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of cardiac conditions, improving patient outcomes.
-
Remote patient monitoring:
IoT devices can monitor patients’ health remotely. Thus, enabling healthcare providers to track their health status in real-time. This can reduce the need for in-person visits, improving patient convenience and reducing healthcare costs.
For example, IoT in healthcare enables remote monitoring of patients with conditions like diabetes. It lets healthcare providers detect issues early and adjust treatment plans. Furthermore, this reduces hospital readmissions and improves patient outcomes.
-
Predictive maintenance of medical equipment:
IoT technology allows healthcare facilities to monitor the performance of their medical equipment in real-time. Thus, by connecting sensors to these devices, hospitals can track various parameters. These include temperature, pressure, and usage patterns continuously.
For example, IoT connectivity can monitor MRI performance. They detect issues before they become serious and schedule maintenance proactively. This can cut downtime. Additionally, It will improve the availability of medical equipment. Thus, it will ensure that patients get timely, high-quality care.
-
Real-time communication and collaboration:
IoT in healthcare plays a crucial role in facilitating real-time communication and collaboration among healthcare providers. In simple terms, IoT helps doctors and nurses communicate better and work together more efficiently.
Therefore, by linking different medical devices and systems through IoT, they can quickly get the information they need about a patient
For example, telemedicine platforms rely on IoT devices. They enable remote consultations between healthcare providers and patients. This reduces the need for in-person visits and improves access to care. Furthermore, real-time communication between healthcare providers can also improve care coordination.
-
Reduction in healthcare costs:
IoT, or the Internet of Things, helps healthcare save money by making things run smoother. Think of it like this: in hospitals and clinics, some devices can talk to each other and share important information.
For example, they can keep track of how many medical supplies are left or if a machine needs fixing. Thus, by doing this, hospitals can avoid spending too much on things they don’t need or big repairs that could have been prevented.

What are the Uses of IoT in Healthcare?
The use of IoT in healthcare is rapidly expanding. It has many exciting applications. They can improve patient outcomes and make healthcare delivery more efficient. Here are some of the key uses of IoT in healthcare:
1. Wearable health devices:
IoT application development has reached remarkable levels of innovation. Wearable health devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, are a popular application of IoT in healthcare. These devices can collect and analyze data on a patient’s physical activity.
Moreover, they are also capable of analyzing heart rate, sleep, and other health metrics. This data can then be used to create personalized health plans. Therefore, it enables patients to take a more active role in managing their health.
2. Remote patient monitoring:
Remote patient monitoring using IoT devices enables healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health status in real-time, regardless of their location. This can reduce the need for in-person visits. Furthermore, IoT in healthcare allows providers to detect potential health issues early, improving patient outcomes.
For example, remote patient monitoring can be used to monitor patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes or heart disease. Thus, ensuring that they receive timely and appropriate care.
3. Connected medical equipment:
IoT in healthcare can be used to connect medical equipment, such as hospital beds and infusion pumps, to the internet. This enables real-time monitoring of equipment performance, predictive maintenance, and automated alerts in case of malfunctions.
Thus, This can improve the availability of medical equipment, reduce downtime, and ensure that patients high-quality care at the right time.
4. Smart hospital infrastructure:
IoT in healthcare can be used to create smart hospital infrastructure. This includes building automation systems, energy management systems, and patient flow management systems.
This can improve operational efficiency, reduce waste, and provide a more comfortable and safe environment for patients.
5. Telemedicine:
Telemedicine is a rapidly growing application of IoT in healthcare, enabling remote consultations between healthcare providers and patients. As a result, this improves care access. It helps patients who live in remote or underserved areas. Moreover, It also reduces the need for in-person visits. This improves patient convenience and cuts healthcare costs.
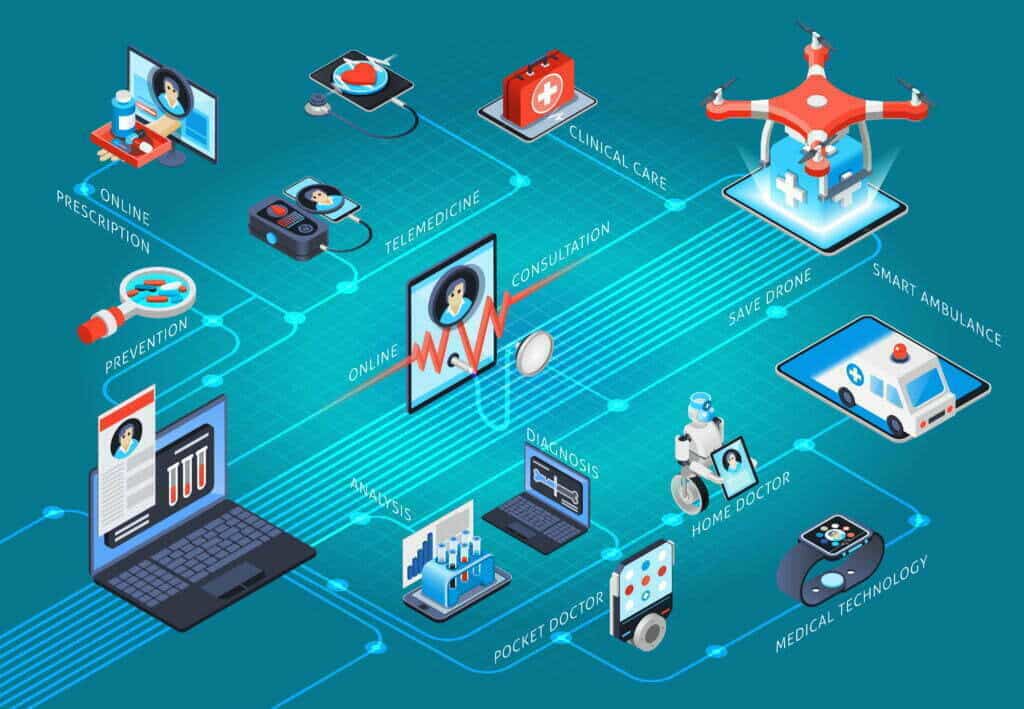
What are the Examples of IoT devices used in healthcare?
IoT application development in healthcare is revolutionizing patient care by providing real-time monitoring, and remote access to medical services. Furthermore, it enhances treatment options through interconnected devices.
Wearable Devices: Wearable devices are a great example of IoT in healthcare. Devices such as fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor a range of health metrics such as heart rate, steps taken, and sleep patterns. These devices can help patients track their health data. Moreover, patients can share it with healthcare providers for remote monitoring.
Remote Patient Monitoring Systems: These systems can be used to monitor patients who are recovering at home after a hospital stay or have chronic conditions. They can track vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels. Furthermore, it can alert healthcare providers if there are any significant changes.
Smart Pills: IoT in healthcare is not only limited to wearables and monitoring. Smart pills contain sensors that can track medication usage and transmit data to a smartphone or other device. This can help ensure patients are taking their medication correctly. Furthermore, smart pills can alert healthcare providers if a patient misses a dose.
Smart Inhalers: These devices can track medication usage for asthma and COPD patients. Thus, providing real-time data on usage patterns and medication adherence. This can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans and identify potential issues before they become more serious.
Telemedicine Platforms: Telemedicine platforms enable healthcare providers to connect with patients remotely using video conferencing technology. This can be particularly useful for patients who live in remote areas or have mobility issues. Therefore, it allows them to receive care without leaving their homes.
What are the Challenges of IoT in Healthcare
Imagine you are a chef and you have decided to introduce a new ingredient to your signature dish. However, this ingredient requires special handling and preparation, and its addition may impact the overall taste and texture of the dish.
Similarly, introducing IoT in healthcare can be like adding a new ingredient to a recipe. It requires careful consideration of how the ingredient will impact the outcome and what steps need to be taken to ensure its successful integration.
Here are some of the challenges of IoT in healthcare:
1. Security concerns:
Just as a chef needs to ensure the safety of their ingredients to prevent contamination. Healthcare providers need to keep IoT devices secure to prevent cyber threats and data breaches. This includes implementing secure data storage and transmission protocols. Moreover, it also includes ensuring the devices themselves are protected from hacking attempts.
2. Data privacy:
A chef needs to protect their recipe from being stolen. Similarly, Healthcare providers need to ensure the privacy of patient data collected by IoT in healthcare devices. This includes ensuring that patient data is collected and stored securely and that patients have control over their data and how it is used.
3. Interoperability issues:
Adding IoT devices to existing healthcare systems can be hard. The devices may use different protocols and data formats. Just like a chef must ensure all the recipe’s ingredients fit, healthcare providers must ensure that IoT devices can talk to each other and existing healthcare systems.
4. Regulatory compliance:
In the highly regulated healthcare industry, IoT devices must comply with numerous regulations and standards. Just as a chef follows food safety rules to keep customers safe, healthcare providers must ensure that IoT devices meet regulations. These regulations include guidelines set by HIPAA and the FDA.
5. Resistance to change:
Finally, some customers may resist trying a new dish with a new ingredient. Similarly, healthcare providers may face resistance from patients, staff, or stakeholders when introducing IoT devices.
Thus, IoT in healthcare may require careful communication and education to address concerns and build support for the adoption of new technology.

Future of the (Internet of Things) IoT in Healthcare
The future of IoT in healthcare is exciting and holds enormous potential for innovation and growth. New trends and tech, like edge computing, AI, and 5G networks, are already shaping healthcare’s future. Subsequently, the possibilities for future development are vast.
For instance, Edge computing is a technology that processes data at the edge of the network, closer to the source of the data. This technology has big implications for IoT in healthcare.
It can help healthcare providers collect, process, and analyze data in real-time. Furthermore, edge computing enables faster data processing and analysis. It helps healthcare providers make better decisions and improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, Artificial intelligence (AI) is another technology that holds great promise for the future of IoT in healthcare. AI can analyze vast amounts of data and provide insights that can inform patient care decisions.
For example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can help doctors find health issues. Additionally, they can also predict health risks. This helps with earlier care and better treatment.
5G networks are also poised to transform the healthcare industry by enabling faster data transfer, lower latency, and more reliable connectivity. 5G networks let healthcare providers quickly transfer large data and get real-time insights. Thus, this lets them make faster, more informed decisions.

How IoT is transforming other industries?
Till now, we’ve seen how IoT in healthcare can improvise and streamline healthcare operations and delivery. Similarly, IoT is changing business processes in many other industries. It provides real-time data to improve ROI, streamline operations, and deliver better results to customers.
As IoT in healthcare continues to develop, we can expect to see even more use cases in the future. Let’s see some of the use cases of IoT in other industries.
1. Manufacturing
IoT is transforming the manufacturing industry by enabling companies to collect and analyze data in real time. According to a report by McKinsey, IoT applications in manufacturing have the potential to generate up to $3.7 trillion in economic value by 2025. Manufacturers are using IoT sensors.
They use them to monitor machine conditions and predict when to do maintenance. Furthermore, they also use them to optimize production. This can help companies reduce downtime, minimize waste, and increase efficiency.
2. Retail
IoT is transforming the retail industry by providing companies with real-time data on customer behavior. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market for IoT in retail is expected to reach $35.6 billion by 2025.
IoT sensors can monitor foot traffic, track customer movements, and analyze shopping behavior. This can help retailers. Moreover, It can help them optimize store layouts and manage inventory better. Thus, It can also help them give customers personalized experiences.
3. Agriculture
IoT is revolutionizing the agriculture industry by enabling farmers to monitor crop growth and soil conditions in real-time. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for IoT in agriculture will reach $20.9 billion by 2025.
Furthermore, IoT devices can monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and weather conditions. Thus, helping farmers anticipate and mitigate risks such as frost, drought, or pests.
4. Transportation
IoT is transforming the transportation industry by providing companies with real-time data on vehicle conditions and location. A report by MarketsandMarkets says the global market for IoT in transportation will reach $143.93 billion by 2025.
This growth in the IoT transportation market means companies are using technology to improve how they move things around. With IoT, they can keep track of their vehicles and see what condition they’re in at any time. Thus, IoT is making transportation smoother.
5. Energy
IoT is revolutionizing the energy industry by enabling companies to monitor energy usage in real time. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for IoT in energy will reach $22.34 billion by 2025.
IoT sensors can be used to monitor energy consumption. Moreover, it can also be used to detect energy waste and optimize energy usage. This can help companies reduce energy costs, minimize waste, and improve sustainability.
Also Check: Why Brands need Cloud Infrastructure Security?
Conclusion: IoT in Healthcare
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by improving patient care and outcomes. Brands can use IoT services in many ways. They can use it for health wearables and remote patient monitoring.
Also, for connected medical equipment, smart hospital infrastructure, and telemedicine. But, there are also challenges. These include security, privacy, compatibility, regulation, and resistance to change.
advansappz is a leading IT and AI consulting company that specializes in IoT development services for the healthcare industry. If you’re looking to integrate IoT into healthcare devices, get in touch with our experts today.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
What is IoT in Healthcare?
IoT in healthcare means using internet-connected devices to gather and share health data for better patient care.
How is IoT being used in healthcare?
In healthcare, IoT is monitoring patients remotely, tracking vital signs with wearables, and improving efficiency in medical processes.
What are the IoT products in healthcare?
IoT products in healthcare include wearable health monitors, remote patient monitoring systems, and smart medical equipment.
How has IoT affected the healthcare industry?
IoT has improved patient monitoring, access to care, and treatment options. Moreover, it also enhances operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
How to control IoT devices?
Users can control IoT devices using mobile apps, web interfaces, voice commands, or centralized IoT platforms.