Streamlining the SAP Service Activation process is crucial for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) solutions. SAP, renowned for its intricate and multifaceted software ecosystem, plays a pivotal role in transforming businesses digitally.
This encompasses various functions, including enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management. However, the activation and configuration of SAP services can be intricate and time-consuming, often marred by challenges such as errors, delays, and operational disruptions.
Organizations must employ strategic methods and best practices to streamline their activation processes to surmount these obstacles and ensure a seamless transition to SAP. One key strategy involves standardizing processes. Organizations can minimize errors and inconsistencies by establishing precise and uniform procedures for SAP activation, ensuring a smoother and more reliable deployment.
Streamlining the SAP Service Activation Process involves strategic planning, technology utilization, and teamwork. By adopting these strategies and best practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of SAP solutions, drive operational efficiency, and pave the way for digital innovation.
This article delves into the strategies, tools, and methodologies that empower businesses to optimize their SAP Service Activation Process, enhance productivity, and drive innovation.
What is SAP Activation Methodology?
The SAP Activate methodology is a structured approach employed for the planning and execution of intricate SAP solutions. Nestled within the broader SAP Activate framework, its primary aim is to enhance the quality and outcomes of SAP projects. Following the roadmap outlined by this methodology empowers project managers to implement SAP solutions more seamlessly. Within the SAP Activate framework, three key pillars combine to assist project managers in leveraging SAP solutions effectively to attain their business objectives. These pillars encompass SAP Best Practices, Guided Configuration, and the SAP Activate Methodology.
SAP Best Practices
Being a prominent player in enterprise software, SAP has harnessed its vast knowledge and expertise to craft readily deployable business processes finely tuned for SAP S/HANA. This forms the foundational pillar of the SAP Activate framework. Accessible via the SAP Best Practices Explorer, these encompass SAP’s standardized business process flows, roles, responsibilities, and test scripts. These can be seamlessly integrated with an organization’s unique processes.
Guided Configuration Guidance
Guided configurations simplify the task of configuring SAP systems for both consultants and customers. SAP is committed to the ongoing development of standardized configurations, fostering global adoption and adherence to industry best practices in business process execution.
SAP Activate Methodology
The SAP Activate Methodology is at the forefront of project implementation methodologies and is dedicated to delivering SAP updates and solutions. With the flexibility to choose from 15 solution-specific roadmaps, this methodology is designed to continuously elevate project quality and enhance the success rate of SAP projects and migrations.
SAP Activate Methodology Roadmap
SAP Activate for SAP S/4HANA
SAP Activate for SAP S/4HANA is tailored for organizations implementing or migrating to SAP S/4HANA, SAP’s advanced ERP suite. It provides a structured approach to effectively plan, execute, and deploy SAP S/4HANA solutions, ensuring a smooth transition from older SAP systems or legacy ERP platforms. It assists in leveraging the advanced capabilities of SAP S/4HANA for streamlined business processes, real-time analytics, and improved user experiences.
SAP Activate for SAP Cloud Solutions
SAP Activate for SAP Cloud Solutions is designed for projects involving SAP’s cloud-based solutions like SAP SuccessFactors, SAP Ariba, or SAP Hybris. It offers guidance on efficiently adopting, configuring, and integrating these cloud solutions into an organization’s landscape. It helps organizations leverage SAP’s cloud offerings’ scalability, flexibility, and innovation potential for HR, procurement, and customer engagement.
SAP Activate for SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)
SAP Activate for SAP BTP is for projects utilizing SAP BTP, a platform for building applications, integrating data, and extending SAP solutions. It guides organizations in developing, deploying, and managing applications and services using SAP BTP. It facilitates the creation of custom applications, data integration, and analytics, enabling organizations to harness the power of data and emerging technologies.
SAP Activate for SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
SAP Activate for SAP IBP targets projects implementing SAP Integrated Business Planning, a supply chain planning and optimization solution. It guides the implementation process, data integration, and best practices for supply chain planning. It helps organizations improve supply chain visibility, demand forecasting, and inventory management, leading to more efficient and responsive operations.
SAP Activate for SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC)
SAP Activate for SAP AC focuses on implementing SAP Analytics Cloud, a data visualization, reporting, and analytics solution. It covers data integration, model creation, dashboard development, and the utilization of SAC for data-driven decision-making. It enables organizations to harness the power of data by creating interactive dashboards, performing advanced analytics, and sharing insights across the organization.
Each of these SAP Activate methodologies is tailored to specific project types and SAP solutions, offering a structured approach to ensure successful implementation and optimization of the respective SAP technologies.
Strategies for Streamlining SAP Activation
Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration involve using technology to automate repetitive and manual tasks in the SAP activation process. Orchestration refers to coordinating these automated tasks into end-to-end workflows. Automation reduces the time and effort required to perform routine tasks, such as software deployments, configuration changes, and system monitoring. Automation reduces the risk of human error, leading to more consistent and error-free SAP activations. Automated processes can execute tasks much faster than manual methods, accelerating the activation process and using scripts or tools to automate software installations, configuration changes, and data migrations—orchestration tools like SAP Solution Manager or third-party solutions to coordinate these tasks into seamless workflows.
Pre-Activation Testing
Preactivation testing involves comprehensive testing before implementing SAP changes or new modules in a production environment. It helps identify and address potential issues, errors, or conflicts before they impact the live system, reducing downtime and operational disruptions. By uncovering issues in advance, organizations can mitigate risks associated with SAP activation, ensuring a smoother transition. It ensures the SAP solution functions as intended, meets business requirements, and delivers expected performance. Unit testing to validate individual components, integration testing to verify interactions between different SAP modules, and user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the solution aligns with user expectations.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC is a security strategy that controls access to SAP systems based on roles and responsibilities. It ensures that only authorized individuals can perform specific tasks during the SAP activation process. RBAC enhances the security of SAP systems by restricting access to sensitive functions and data. It helps track and audit user actions, providing accountability in case of unauthorized changes or data breaches. By defining role-specific permissions, RBAC streamlines the activation process by allowing authorized personnel to perform tasks relevant to their roles. Assigning roles such as “Administrator,” “Developer,” or “Business Analyst” with corresponding permissions in SAP systems. Ensuring that only administrators can make configuration changes while developers focus on coding and analysts perform data analysis.
Real-time Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time monitoring involves continuously tracking the health and performance of SAP systems during and after activation. Alerts are set up to notify relevant teams of anomalies or potential issues. Real-time monitoring enables the rapid detection of performance bottlenecks, security breaches, or system failures, allowing teams to take immediate action. Alerts can help prevent extended downtime by addressing issues as soon as they arise, minimizing the impact on business operations. Monitoring data can be used to optimize SAP systems continuously, ensuring they perform at their best. Implementing monitoring tools like SAP Solution Manager or third-party solutions to track system metrics, setting up alerts for specific performance thresholds or security breaches, and establishing incident response protocols.
These strategies collectively contribute to a more efficient and reliable SAP activation process, reducing risks, minimizing errors, and accelerating the deployment of SAP solutions.
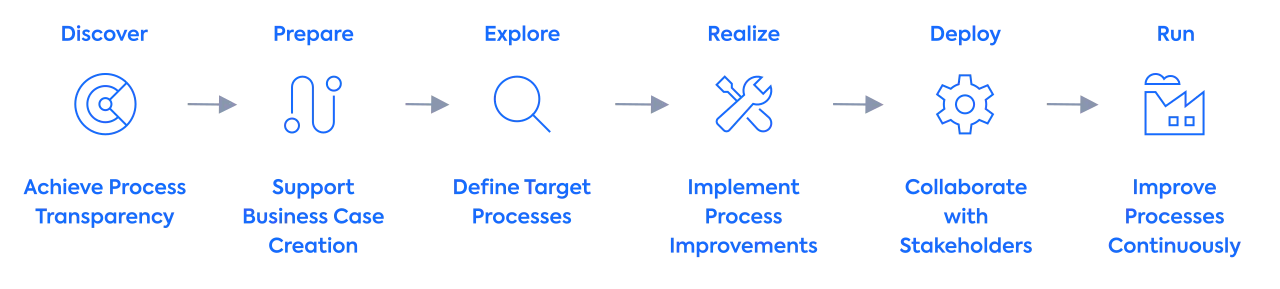
SAP Activate methodology phases
Discover phase
The Discover phase of the Activate methodology involves crafting a roadmap and devising implementation strategies. SAP provides a complimentary trial period for cloud and on-premise installations with preconfigured best practice scenarios. During this phase, business users can assess S/4HANA on-premise (30-day trial) and cloud (14-day trial) alternatives, evaluating diverse business processes throughout the organization. This exploration aids in the formulation of a business case for the adoption of S/4HANA.
Prepare phase
In the Prepare phase, the project team initiates essential planning and preparatory tasks to kickstart the project. The section delineates project objectives and scope during this stage and develops a plan. Moreover, roles and responsibilities within the project team are clearly defined. This phase encompasses various activities, including establishing project standards, organizational structure, and governance, assessing the customer team, implementing project management procedures, setting up monitoring and reporting mechanisms for project delivery, team familiarization, and ensuring system access.
Explore phase
The project team ensures that business requirements align with the solution and project scope during the Explore phase. This phase utilizes a pre-configured solution based on SAP best practices tailored to the customer’s needs, facilitating solution validation workshops. Integration with legacy systems begins, and various tasks are undertaken, including a review of data requirements, data cleansing, configuration value definition, and identification of master data and organizational setup needs.
Realize phase
The project team employs a series of iterations to construct and test a comprehensive business and system environment, guided by insights gathered from earlier stages in the Explore phase. Business users conduct extensive end-to-end solution testing and formulate a cutover plan. Furthermore, they engage with stakeholders to walk through solution processes. This phase also encompasses tasks such as solution configuration, preparation for change management, and end-user training. Additionally, the project team fulfills various responsibilities in this phase, including Data Volume Management (DVM), data migration and verification, security implementation, IT infrastructure setup, and sizing and scalability verification.
Deploy phase
The Deploy phase holds paramount importance within the Activate methodology. During this critical stage, the project team readies and implements the system for its production release, commonly known as the Go-Live phase. The team meticulously follows the cutover plan, facilitating the transition of business operations to the new system while shifting from implementation support to production support. The team executes the final dress rehearsal and production cutover as previously planned in earlier phases to ensure a seamless transition. This phase culminates with hyper-care activities, providing diligent post-system release support.
Run phase
The Run phase represents the ultimate stage in the Activate methodology. During this phase, the project team concludes all ongoing activities and transfers all pertinent information to the support team. Additionally, the team remains engaged in addressing any last-minute system bugs or errors. Integration with the SAP Solution Manager for operational, monitoring, and support purposes is finalized. Ultimately, the project team formally closes the project and delivers all essential documents to the business owners.
Challenges in the SAP Service Activation Process
Configuring the service components of the SAP landscape correctly
Configuring SAP service components correctly can be a complex task due to the intricate nature of SAP solutions. Incorrect configuration can lead to operational disruptions, errors, and performance issues. To address this challenge, businesses should adopt best practices for SAP configuration. This includes having skilled SAP administrators who thoroughly understand the system’s requirements, following SAP’s documentation and guidelines, and conducting rigorous testing to validate the configurations. Regular updates and reviews of configurations are also essential to keep them aligned with changing business needs.
Managing dependencies between different services
SAP landscapes often consist of multiple interconnected services and components. Managing dependencies between these services can be challenging, especially when changes or updates are required. To mitigate this challenge, businesses should implement effective change management practices. This includes maintaining a detailed inventory of all services and their dependencies, conducting impact assessments before making changes, and establishing change control processes to ensure that changes are properly planned, tested, and documented. Automated monitoring and alerting systems can help proactively identify and address dependency issues.
Ensuring that all components are correctly configured to avoid issues during service activations
The correct configuration of all SAP components is critical to a smooth service activation process. Any misconfiguration can lead to errors, delays, and operational disruptions. To overcome this challenge, businesses should establish a rigorous quality assurance and testing process. This includes conducting comprehensive pre-activation testing to identify and address configuration errors or inconsistencies. Creating detailed checklists and validation procedures can help ensure all components are correctly configured before activation. Regular audits and reviews of configurations are also essential to maintain consistency and accuracy.
Customization needs, data migration, and cleansing
Many organizations require customization to align SAP solutions with their unique business processes. Customization adds complexity to the activation process, leading to longer implementation timelines and increased costs. Transferring existing data into the new SAP system can be complex and time-consuming. Data quality issues, mapping, and cleansing are common challenges during migration, which can affect the accuracy and reliability of the new system. SAP activation projects often require skilled SAP consultants and project resources. Finding and retaining the right talent can be challenging, especially for organizations in competitive job markets.
Effective testing and validation strategies are crucial in overcoming common challenges in SAP service activation. These strategies involve skilled personnel, adherence to best practices, thorough documentation, and proactive monitoring to ensure that SAP services work optimally and deliver the expected business benefits. By addressing these challenges proactively, businesses can minimize disruptions and maximize the value of their SAP investments.
Also Check: Best practices for Mulesoft SAP integration
Final Words
The SAP Service Activation process is purpose-built to assist SAP customers in implementing and enhancing critical business software, especially suited for SAP S/4HANA implementation and conversion projects. This methodology accelerates complex solution implementation with well-defined directives and success-oriented roadmaps. Tools like LeanIX EAM provide valuable insights to SAP Architects and Project Managers. Streamlining this process is imperative for organizations aiming to efficiently unlock SAP solutions’ potential. SAP’s software ecosystem, including ERP, CRM, and supply chain management, is central to digital transformation but often comes with complex challenges like errors and delays.
Organizations should employ strategic approaches, advanced solutions from experts like advansappz to overcome these obstacles. These empower businesses to optimize the SAP Service Activation Process, enhancing productivity and fostering innovation. By efficiently streamlining this critical process, organizations harness the transformative power of SAP solutions, enabling them to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. In summary, SAP Service Activation is a crucial methodology for successful SAP projects, and organizations should focus on its efficient implementation to drive digital transformation and gain a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions
SAP services encompass a wide range of offerings provided by SAP, a leading software company. These services include consulting, implementation, customization, and support for SAP software solutions. They are designed to help businesses optimize their operations, manage their data, and streamline processes. SAP services also cover training and education to empower users and maximize the benefits of SAP software. Overall, SAP services aim to enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness for organizations using SAP solutions.
SAP Consulting Services refer to specialized advisory and implementation support offered by experts in SAP software solutions. These services assist businesses in optimizing their SAP systems, configuring software to meet specific needs, and ensuring smooth operation. SAP consultants provide guidance on best practices, integration, and customization to maximize the benefits of SAP technology for organizations.
An SAP software tool is a specialized software application developed by SAP SE, a multinational software corporation based in Germany. These tools are designed to help businesses manage various aspects of their operations, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and more. Examples of SAP software tools include SAP ERP, SAP S/4HANA, SAP Business One, and SAP Customer Experience (CX) solutions. These tools are widely used by organizations globally to streamline their processes and improve efficiency.
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) is primarily used for enterprise resource planning (ERP) and business process management. It helps organizations manage various aspects of their business, including finance, human resources, procurement, supply chain, and customer relationship management. SAP software streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and improves overall efficiency, making it a popular choice for large and complex businesses looking to optimize their processes and data management.