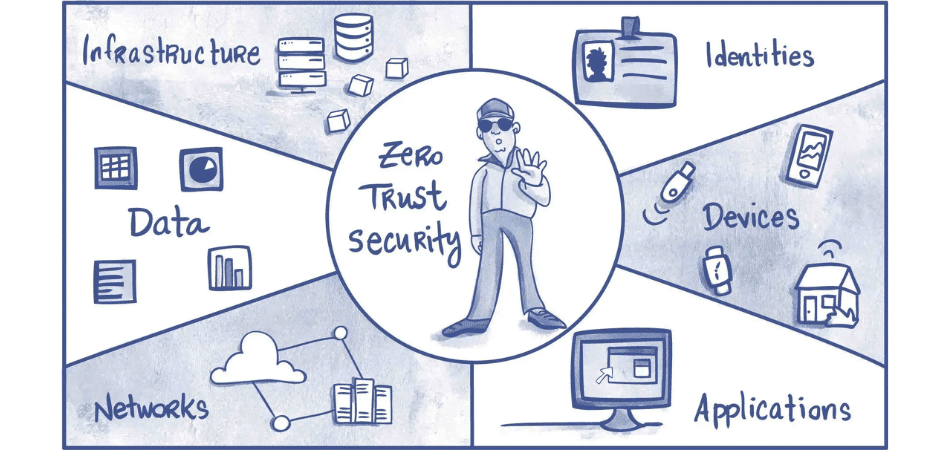
Enterprise cybersecurity is one of the most pressing concerns for businesses today. With the proliferation of cyber attacks, data breaches, and other forms of malicious activity, companies are grappling with how to secure their networks and data. In response, many businesses are turning to Zero Trust Policy, a security approach that requires verification before granting access to network resources and data.
What does Zero Trust Policy Mean for Cybersecurity?
A zero-trust policy is a cybersecurity approach that requires verification before granting access to network resources and data. Unlike traditional security approaches that rely on perimeter-based defences, zero trust policy assumes that all network traffic is potentially malicious and requires verification before granting access.
Under a zero-trust policy, users must authenticate their identity and meet other security requirements before accessing network resources and data. This authentication process may involve a combination of factors such as user credentials, device health, network location, and behavioral analysis.
Once the user has been authenticated, they are granted access to only the resources and data needed to do their jobs. This approach helps limit the attack surface by compartmentalizing network traffic and granting access only to the resources necessary for business operations.
By adopting Zero Trust Policy, businesses can boost their security and reduce the risk of data breaches and other cyber attacks. However, Zero Trust Policy is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The future of the Zero Trust Policy in enterprise cybersecurity is evolving as businesses adopt new technologies and strategies to protect their networks and data.
Let us understand a few emerging trends shaping the future of the Zero Trust Policy in enterprise cybersecurity.
Emerging Trends of Zero Trust Policy in Cybersecurity
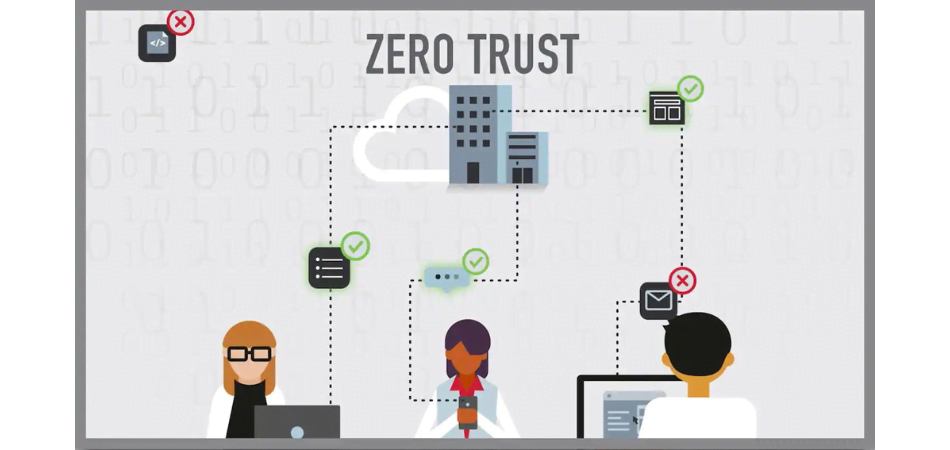
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Another trend in Zero Trust Policy is the increased use of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA is a security approach that requires users to provide multiple verification forms before granting access. By requiring users to provide various forms of authentication, including a password and a fingerprint scan, MFA helps to reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. - Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are technologies increasingly used in cybersecurity to detect and prevent cyber threats. In the Zero Trust Policy context, AI and ML can be used to identify anomalies in network traffic, detect suspicious behavior, and identify potential security threats. By using AI and ML, businesses can increase their security posture and stay ahead of cybercriminals. - Microsegmentation:
Microsegmentation is an approach that involves dividing a network into smaller segments and restricting access between them. This approach helps to limit the spread of cyber attacks by compartmentalizing network traffic. In addition, by implementing micro-segmentation, businesses can reduce the attacks, making it harder for hackers to move laterally once they gain access to a single segment. As a result, micro-segmentation is an effective way to enhance enterprise cybersecurity. - Enhanced Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Identity and Access Management is a security approach that manages user identities and permissions to access network resources and data. In Zero Trust Policy, IAM is an essential part of the security approach, as it ensures that only authorized users have access to the network resources and data. Enhanced IAM involves using advanced technologies such as biometric and behavior-based authentication to ensure only authorized users can access network resources and data. - Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):
One of the emerging trends in the Zero Trust Policy is the shift to Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). Unlike traditional remote access methods such as virtual private networks (VPNs), ZTNA focuses on granting secure access to applications and data based on user identity, device health, and other contextual factors. ZTNA helps reduce the attack surface by providing access only to the resources users need to do their jobs, improving enterprise cybersecurity.
While these emerging trends shape the future of the Zero Trust Policy in enterprise cybersecurity, businesses must also consider the unique security risks and challenges they face. For example, companies that operate in highly regulated industries such as healthcare or finance may require additional security measures to comply with regulations. Additionally, businesses that rely heavily on cloud-based applications and services may need to adopt different Zero Trust Policy strategies to secure their data.
Cybersecurity is a concern for all sectors, individuals, organizations or governments, but enterprises should be more careful about it for many reasons. Enterprises can affect their financial stability and disrupt operations if a cyber threat hits them. For instance, if an organization delivers food, they might have their consumers’ data, address details, food choice, phone number, and many more details. If this data is stolen by a cyber attack and shipped to a competitor organization, it would be a commercial risk for the food company.
Additionally, it also affects the consumers’ right to privacy; therefore, it poses a considerable problem to the enterprise. Consequently, they must consider it seriously and appoint a cybersecurity agent to manage critical sensitive data. Now, the question arises: What enterprise cybersecurity threats may an organization face? So, let’s delve into the intricacies and discover the top 5 cybersecurity threats.
Advancements in Zero Trust Policy
Zero Trust Policy is a security approach that assumes that all users, devices, and applications are potentially untrustworthy and must be verified and authenticated before being granted access to resources. Over time, Zero Trust Policy has evolved to include more advanced features and capabilities to meet the changing needs of organizations. Here are three critical advancements in Zero Trust Policy:
Identity-based Zero Trust Policy:
Identity-based Zero Trust Policy is a security approach focusing on the identity of users, devices, and applications before granting access to resources. According to a report by Forrester, 49% of organizations plan to invest in identity and access management (IAM) solutions to support their Zero Trust initiatives. Additionally, the report states that organizations that adopt an identity-centric approach are better equipped to prevent data breaches and have a 50% lower risk of a data breach than organizations that don’t.
Continuous Zero Trust Policy:
A continuous Zero Trust Policy involves continuously monitoring and verifying the trustworthiness of users, devices, and applications throughout their access lifecycle. According to a report by Cybersecurity Insiders, 49% of organizations plan to adopt a continuous Zero Trust Policy within the next 12 months, while 34% have already adopted this approach. The report also states that a constant Zero Trust Policy helps organizations detect and prevent unauthorized access attempts more quickly, with 49% of respondents reporting that they had improved their incident detection and response times with a continuous Zero Trust Policy.
Zero Trust Policy in the Cloud:
Adopting Zero Trust Policy for cloud-based resources becomes essential as more organizations move their infrastructure and applications to the cloud. According to a report by TechValidate, 64% of organizations surveyed said they are either already implementing or planning to implement Zero Trust Policy in the cloud. Additionally, the report found that 74% of respondents said they were concerned about the security risks associated with cloud adoption, and 75% said they saw Zero Trust Policy as a way to mitigate those risks. Overall, these statistics demonstrate the growing importance of the Zero Trust Policy in cloud security.
Future Trends in Zero Trust Policy
Zero Trust Policy has become increasingly important in enterprise cybersecurity, and new trends are emerging as technology evolves. Here are three critical future trends in Zero Trust Policy:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for AI in cybersecurity is expected to reach $38.2 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.3% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of AI and ML in the Zero Trust Policy to improve threat detection and response. Additionally, a report by IBM found that organizations that use AI and ML in their cybersecurity practices can reduce the cost of a data breach by up to 38%.
Increased adoption of Zero Trust Policy:
As organizations recognize the importance of the Zero Trust Policy in cybersecurity, its adoption is expected to continue to grow. According to a survey by Pulse Secure, 62% of organizations surveyed have already implemented or are in the process of implementing the Zero Trust Policy, while another 31% plan to implement it within the following year. Additionally, a report by Cybersecurity Insiders found that 60% of organizations surveyed plan to increase their investment in Zero Trust Policy next year.
Focus on Data Privacy:
The focus on data privacy is becoming increasingly important, and Zero Trust Policy can play a crucial role in protecting sensitive data. According to a report by IDC, worldwide spending on data privacy solutions is expected to reach $2.3 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 17.3% from 2019 to 2023. Additionally, a survey by Cisco found that 84% of consumers said they are concerned about the privacy of their data and want to know how it is being used. As a result, organizations are expected to focus more on data privacy and implement Zero Trust Policy as part of their data protection strategy.
Also check: Cybersecurity Trends to Watch in 2023
Final Words
As businesses rely more on digital technologies and data-driven operations, implementing a zero-trust policy will become increasingly critical to securing their operations and protecting their valuable assets from cyber threats. By adopting a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, businesses can stay ahead of potential security threats and ensure the safety and security of their customers, employees, and partners.
advansappz is one of the reliable names in offering trusted and secure cloud environments and cybersecurity assistance for various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Zero trust is the future because it offers a more effective approach to cybersecurity. It assumes that no user or device should be automatically trusted, even if they are within the network perimeter. Instead, zero trust implements strict access controls and continuous verification to ensure security. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, especially in today’s increasingly complex and interconnected digital landscape.
Yes, Zero Trust is considered to be the future of cybersecurity. Zero Trust is an approach to security that challenges the traditional perimeter-based model, which assumes that everything inside the network is trusted and everything outside is not. In contrast, Zero Trust assumes that no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter.
The concept behind Zero Trust is to verify and authenticate every user and device attempting to access an organization’s resources, regardless of their location or network environment. This approach reduces the risk of data breaches and insider threats by implementing strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and authentication mechanisms.
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, mobile devices, and remote work arrangements, the traditional security perimeter becomes less effective. Zero Trust addresses this shift by focusing on securing individual devices, users, and data regardless of their location. By doing so, it provides a more robust and adaptable security framework for the evolving technology landscape.
Furthermore, Zero Trust aligns with the principles of least privilege and defense in depth, which are essential for modern cybersecurity. It promotes the principle of granting the minimum necessary access to users, limiting lateral movement within networks, and ensuring that security controls are layered throughout the infrastructure.
While Zero Trust is gaining popularity, implementing it can be a complex process that requires careful planning, architectural changes, and investment in advanced security technologies. Nonetheless, the concept of Zero Trust is increasingly recognized as an effective approach to mitigating cyber risks and securing organizational assets in today’s interconnected and dynamic digital environments.
Zero Trust policy in cybersecurity is a strategic approach that assumes no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter. It challenges the traditional security model of trusting everything inside the network and instead focuses on verifying and authenticating every user and device attempting to access resources.
In a Zero Trust policy, access to resources is granted on a “need-to-know” basis, meaning that users are only given access to the specific resources they require to perform their tasks. This principle of least privilege ensures that even if one part of the network is compromised, an attacker cannot easily move laterally to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
To enforce the Zero Trust policy, organizations implement a variety of security measures such as multifactor authentication, continuous monitoring, encryption, micro-segmentation, and strict access controls. These measures aim to ensure that each user and device is thoroughly authenticated and authorized before accessing resources, regardless of their location or network environment.
By adopting a Zero Trust policy, organizations enhance their cybersecurity posture by minimizing the risk of data breaches, insider threats, and lateral movement within the network. It provides a proactive and adaptive security approach that aligns with the evolving technology landscape and the increasing prevalence of cloud computing, mobile devices, and remote work arrangements.
In summary, a Zero Trust policy in cybersecurity rejects the assumption of trust and implements strict authentication, access control, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure that every user and device is verified before accessing resources, regardless of their location or network context.
The main goal of Zero Trust is to enhance cybersecurity by shifting from a perimeter-based security model to a model that verifies and authenticates every user and device attempting to access resources. The aim is to minimize the risk of data breaches, insider threats, and unauthorized access by assuming that no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location within or outside the network perimeter.
The impact of Zero Trust security is significant in enhancing overall cybersecurity posture. By implementing Zero Trust principles and practices, organizations experience several benefits, including:
-
Improved security posture: Zero Trust mitigates the risk of data breaches, insider threats, and lateral movement within the network by enforcing strict authentication, access controls, and continuous monitoring. This leads to enhanced protection of sensitive data and resources.
-
Enhanced visibility and control: Zero Trust provides organizations with granular visibility into user and device behavior, allowing for better detection of suspicious activities and potential threats. It enables organizations to have a comprehensive view of their network and make informed security decisions.
-
Adaptability to evolving threats: Zero Trust is designed to address the dynamic and ever-changing cybersecurity landscape. It enables organizations to adapt to new threats, technologies, and trends, such as cloud computing, remote work, and mobile devices, by focusing on securing individual devices, users, and data regardless of their location.
-
Compliance and regulatory alignment: Implementing Zero Trust can help organizations meet compliance requirements and align with various industry regulations. The principle of least privilege and strict access controls align with privacy regulations and frameworks such as GDPR and HIPAA.
-
Improved incident response and recovery: Zero Trust allows organizations to detect and respond to security incidents more effectively. With granular visibility and control, organizations can quickly identify and isolate compromised devices or users, limiting the impact of potential breaches and reducing the time to remediate.













